TCP1101: In this assignment, you will implement an assembly language interpreter that will run assembly language instructions: programming Assignment, MMU, Malaysia
| University | Multimedia University (MMU) |
| Subject | TCP1101 programming Assignment |
Assembly Language Interpreter
Introduction:
In this assignment, you will implement an assembly language interpreter that will run assembly language instructions with accordance to a given simplified virtual machine architecture. The interpreter is expected to execute an assembly program and generate a display of the content of the virtual machine after the execution of the program.
The assembly language for the given virtual machine supports various operations such as:
1. Move operations,
2. Mathematical operations,
3. Rotation and shifting operations,
4. Basic I/O operations,
5. Loading data from memory,
6. Storing data to memory.
Virtual Machine Architecture:
The virtual machine includes 7 data general registers and a program counter where each of them is one byte wide (char), 4 flag registers (Overflow, Underflow, Carry, and Zero), and a main memory of 64 bytes.
Your virtual machine architecture will include the following components:
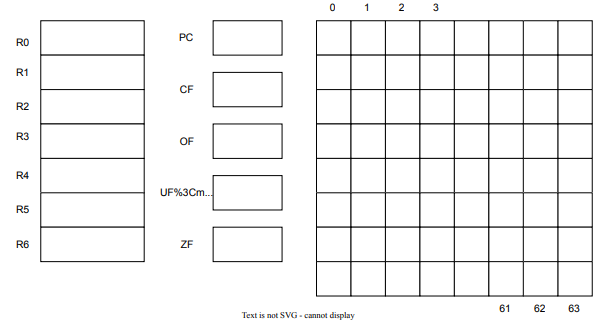
1. Data Registers:3
7 general-purpose data registers: R0, R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R6. Each register is represented as a one byte (8 bits) in size. The contents of these registers are updated after executing each assembly instruction by the runner. These registers can contain signed bytes (values between -128 and 127)
2. Program Counter (PC)
The program counter starts always with the value 0, then it is incremented whenever the runner (interpreter) executes an assembly instruction.
3. Flags:
- Overflow Flag (OF): A single bit flag (or a byte) indicating arithmetic overflow. It is set when an arithmetic operation results in a value greater than 127.
- Underflow Flag (UF): A single bit flag (or byte) indicating arithmetic underflow. Set when an arithmetic operation results in a value smaller than -128.
- Carry Flag (CF): A single bit flag (or a byte) indicating carry in arithmetic operations. Set when an arithmetic operation results in a carry. An addition can generate a value larger then 8 bits, therefore the carry flag is set.
- Zero Flag (ZF): A single bit flag indicating the result of an operation is zero. Set when the result of an operation is zero.
4. Memory:
The memory can be represented as a one-dimensional array of 64 signed bytes. Memory addresses are numbered from 0 to 63. Memory can e accessed only by a load or store operations.
5. Assembly Language Runner (interpreter):
The interpreter reads an assembly program from a “.asm” file (text file). It must execute the instructions sequentially on the virtual machine updating the PC (program counter) after each instruction. At the end of execution, it will produce a dump of all registers and memory to the screen in addition to the output window (results of the I/O operations).
6. The assembly language instructions:
The assembly language is expected to support I/O operations, arithmetic operations, rotation, shifting, loading from memory (direct and register indirect addressing), and storing into memory
Input/Output operations:
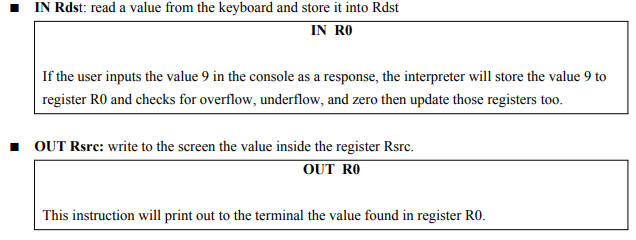
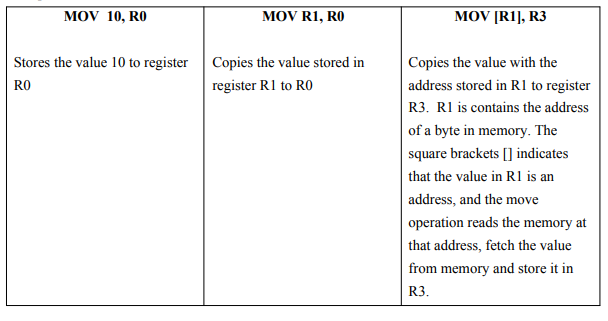
Mov operations:
- MOV Rsrc, Rdst: copies the values stored in the source register to the destination register. The mov operation supports three modes only, these modes are explained in the following 3 examples.
 Stuck in Completing this Assignment and feeling stressed ? Take our Private Writing Services.
Stuck in Completing this Assignment and feeling stressed ? Take our Private Writing Services.
Get Help By Expert
Need assistance with TCP1101 programming Assignment? Our programming assignment helper Malaysia service is here for you. We specialize in providing expert support as your trusted assignment helper. Malaysia students can confidently pay our experts for tailored assistance, ensuring success in their programming endeavors. Trust us to guide you through TCP1101 with confidence and ease.
Recent Solved Questions
- Certified Financial Planner Assignment, UTAR, Malaysia Some weeks ago, you (Danny Lim) a Certified Financial Planner (CFP) and a licensed Financial Planner met your old friend
- FBF1163 Fundamentals of Programming Assignment, UCSI, Malaysia Presume that your class at UCSI finishes at 6:30 pm and you must travel 6 km to reach your home for dinner
- Networks and Networking Assignment, APU, Malaysia As a network engineer working for Ajey Kurnia Berhad, you are required to design and apply an IP addressing scheme
- International Building Control Report, TARC, Malaysia Human effort in the organization is indispensable. It constitutes a complex phenomenon for managers of such organizations
- BMG302/03: Managers can learn how to get the best work out of their business or organization: Organizational Behavior Assignment, WOU, Malaysia
- MPU3223/03: Decision Making Skills Assignment, WOU, Malaysia What are the challenges that you face when making decisions at the workplace
- Exploring Factors Associated with Communication Impairment and Oral Health in the Elderly – Thesis
- Economics Essay, UON, Malaysia India’s income has grown at its slowest rate in almost five years, according to the latest data released by the government
- MPU3412 COMMUNITY SERVICE OUM Assignment Example Malaysia Community service is an important activity to promote goodwill between the community and the environment.
- Strategic Management Assignment, ASB, Malaysia Strategic management is the ongoing planning, monitoring, analysis, and assessment of all necessities an organization



